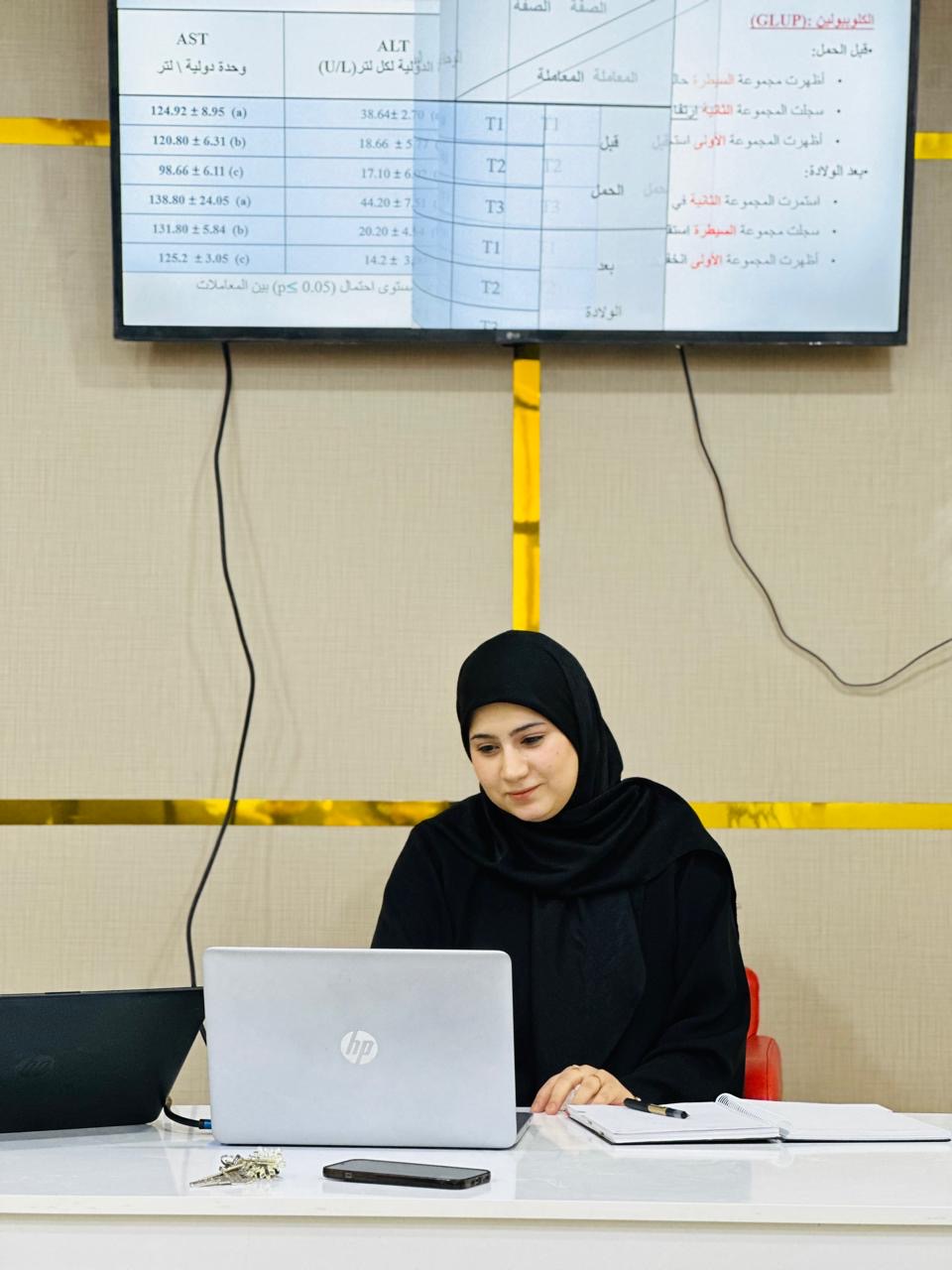
The Qurna College of Education at the University of Basra held a seminar on studying the effect of potassium dichromate on the functions of the thyroid and reproductive glands and some hematological and biochemical parameters in female laboratory rats.
The increasing use of heavy metals in most industrial activities has led to them being considered among the most important environmental pollutants that may cause harm and toxicity to animals and humans. Chromium compounds of all valences are considered basic chemicals that play a role in many industrial and research fields. Among these compounds, potassium dichromate stands out, which is considered a source of concern due to the risks resulting from it in the environment and living organisms. As for food, the amount of chromium is variable and has been accurately measured in relatively few foods. Whole grain products, high-bran cereals, green beans, cauliflower, nuts, and egg yolks are considered good sources of chromium. Processed meat also contains a high percentage of chromium, depending on the processing equipment and method. However, there is no large database of chromium content in food.
The study aimed to know the effect of this substance on the thyroid and reproductive glands, malformed newborns, and also on the liver and spleen.
It included a study of a number of rats, divided into three groups, which were dosed for a certain period, and then laboratory work was conducted on them in terms of anatomy and analysis.
The study recommends avoiding using plastic to store hot materials and conducting other studies with different concentrations to determine the effects on other organs.